
- via the inkjet printer's own software driver
- via a third-party software RIP
When printing via a RIP, use a custom profile for the ink/paper combination used to create the CMYK guide print. Verifiable proofs differ from CMYK guide prints in two important ways:
- They are printed via a certified proofing system (SWOP, Fogra, etc.) Certified proofing systems combine RIP software, inkjet printers, inksets, and proofing paper. More information on SWOP-certified systems is available.
- They contain an industry-standard target such as the 12647-7 Control Strip or the Fogra Media Wedge. By reading the target with a spectrophotometer, the recipient can verify the validity of the proof by confirming that the readings are within a certain tolerance.
Since inkjet prints made from RGB editing spaces will have wider color gamuts than available from an offset press, CMYK guide prints must be "cross rendered" to more accurately predict the final CMYK printing. Cross rendering involves printing to the inkjet proofer using the final CMYK press profile as an intermediate space, thereby limiting the inkjet proofer's color gamut to the gamut of the final CMYK output space. If you use Absolute Colorimetric (or check the "simulate paper color" box in Photoshop CS3), you may more closely simulate the actual press sheet, since the whites will more closely match the duller white of the actual press stock.
Use a proofing paper that simulates the actual printing stock. Viewing conditions for guide prints and proofs should be consistent and ideally match the standards commercial printers use for viewing. A 5000K light booth or Solux low-voltage system is recommended. The current ANSI standard for brightness is 2200 lux, which is roughly equivalent to f16 at ¼-second at ISO 100.
It's possible to create CMYK guide prints or even SWOP-certified proofs with inkjet printers. Photoshop's print dialog can be set to create a guide print. But more accurate SWOP proofs require a RIP. Epson offers professional printers with SWOP-certified ColorBurst RIPs.
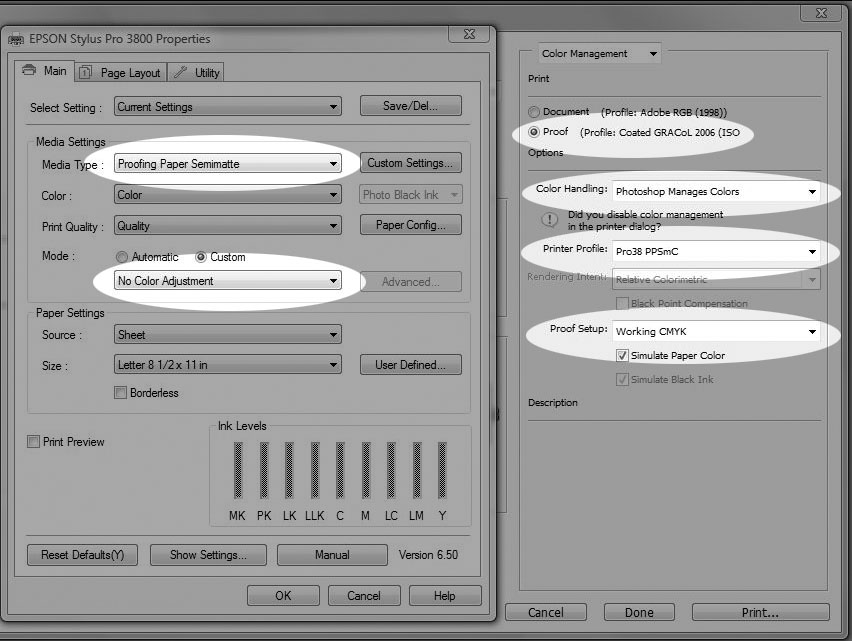
Epson Properties and Photoshop Print Dialog for making a cross rendered CMYK guide print.